Sensor Data Management for Enhanced maintenance safety and efficiency





Maintenance Excellence | Maintenance Strategy | Improve OEE | Pharmaceutical Industry
Goal N°1: Solving organizational challenges
1. Improving communication
2. Time and priority management
Goal N°2: Decrease downtime and improve production lines availability (OEE)
1. Establish exchange of knowledge and standardization of maintenance interventions
2. Optimize interventions performing Root Cause Analysis and providing expert feedback
3. Deliver high quality results that minimizes the need for correction
4. Organize around priorities: communicate supply objectives to the maintenance team, be ready during batch changes or major cleanings
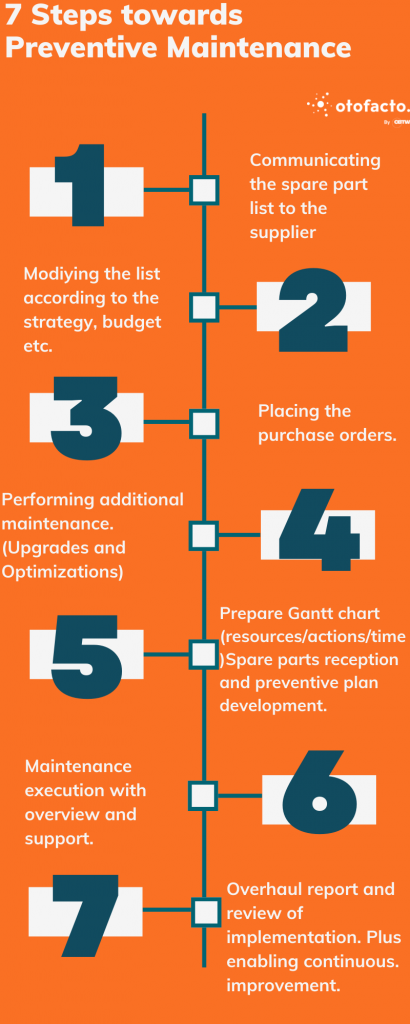
Goal N°3: Execution of preventive maintenance as a part of achieving overall maintenance excellence and enabling continuous improvement
1. Obtaining the needed spare part’s first quotation
2. Modification and final validation of the SP lists
3. Place the purchase orders
4. Planning the extra maintenance actions based on events during production
5. Spare parts reception, printing of preventive plans, prepare Gantt chart (resources/actions/time)
6. Maintenance execution
7. Overhaul report
Our results: Overall results of achieving maintenance excellence
The context:
Our client is a privately owned global pharmaceutical company, specializing in Women’s and Men’s Health and is manufacturing and developing drugs for the treatment of gynaecological, fertility, and obstetrical conditions as well as androgen deficiencies.
The client is a world leader in novel therapies for gynaecology and andrology, pioneer in transdermal gels. It has developed several natural hormone-based therapies over the years.
The client aims to improve technical performance for each line because of the current soar in demand and the pressure from the supply chain to be more efficient, and hence, more competitive and attain customer satisfaction.
The client has 6 productions lines (Tube-bottle-stick) and the aim is to reach
Otofacto partnered with the client to provide expert advisory and consulting service to investigate the sources of failure within the maintenance department and to provide assistance to the maintenance team via both soft and hard skills. This will help the client in achieving maintenance excellence. Furthermore, the plan to develop preventive maintenance at the production lines in the future was also solidified through us.
The challenges of our client:

To achieve the first goal, we implemented the following actions:
1. Improving Communication
2. Time & Priority Management
We addressed the communicational challenges and proposed appropriate solutions.
Purpose
To increase overview of what was happening and find a factor of motivation as a result of improved involvement within the team.
Our implementation
A regular stand-up meeting was set up where the team of technicians at the client was provided up-to-date and right information. This included the issues, developments and tasks concluded by others, KPI status, etc.
Why we implemented this solution
The technicians can better manage the brainstorming and feedback session leading to better outputs as a result of getting the right feedback at the right time.
The results
The overall training level of the technicians increased up to 80% (25% initially). This made the technicians more familiar with the GMP procedures and standards, such as the rules of quality of management, security rules, developing work permit, rules for confined space and for ATEX areas. This was a crucial step towards achieving maintenance excellence.
In addition, the boost in the visual management (pictures and description of technical problems, showing KPIs and actions), allowed the technicians to visualize exactly:
Our implementation
We prioritized tasks for each member of the team, mentioned the bottlenecks and critical points based on the outputs of the last shift’s production report of the technicians, and then we developed a day-to-day plan of what the technician needed to focus on during his shift.
Why we implemented this solution
In this manner, specific problems were dealt with by expert technicians. It prevented technicians from becoming responsible of something else.
For example, if the report mentioned problems with labelling machine, a specific technician with that expertise was tasked to perform a Root Cause Analysis (RCA). Based on the management decision, we can implement intervention solutions (corrective or preventive).
The results
Through this approach the workflow was smoother. Less friction occurred overall.
Team collaboration
In order to increase productivity, motivation and to focus on a shared goal, we instored a collaborative work environment, brainstormed around ideas, shared knowledge and expertise, and gave and received feedback.
To achieve the second goal, we performed the following actions:
1. Establish the exchange of knowledge and standardization of maintenance interventions.
2. Optimizing interventions performing Root Cause Analysis and providing expert feedback
3. Deliver high quality results that minimizes the need for correction.
4. Organize around priorities: communicate supply objectives to the maintenance team, be ready during batch changes or major cleanings.
Our implementation
We promoted Gemba walks between technicians, updated maintenance instructions, and created new ones, if necessary, which validated and displayed machine parameters.
Why we implemented this solution
This enabled us to prevent problems before they occurred. The routine controls behind the Gemba walks (checks and controls) helped us predict symptoms and fails.
Results
This contributed directly in achieving maintenance excellence, which directly contributed to lower downtimes. Now, to solve the issues of the machines, shutdowns were not required anymore.
Our implementation
We implemented basic tools of diagnostic assistance (digitalized technical files, basic machine parameters) to detect the deviation, provide the necessary tools for the technicians, share the current spare part state (excel file for quick search).
Why we implemented the solution
In order for each technician to know how the problems have been solved before, it is crucial to collect the data and digitalize the information. Also, by establishing 6S within workshops we enabled warehouse visibility: we immediately knew which spare parts needed to be purchased and when.
Results
This all inevitably improved time efficiency by preventing time lost due to mismanagement such as looking for tools, figuring out spare parts etc.
Our client, indeed, lowered its mean time to repair (MTTR) thanks to the higher technicity of the members and the better equipment maintenance.
“Mean time to repair (MTTR), sometimes referred to as mean time to recovery, is a metric used to measure the average time it takes to repair a system or piece of equipment after it has failed.” – IBM
Our implementation
We made a standard to maintain the quality and quantity of production, based on management’s factual decisions.
Purpose
– Avoid troubleshooting without placing curative actions.
– Tracing the deviations made from the origin.
Results
Solving the maintenance issues from scratch rather than making corrective actions, to maintain quality and quantity of production.
Our implementation
We set up visual management in the maintenance board (KPI/planning/priorities) and actions for technicians to undertake. This helps them in their decision-making: they know, for example, which line to focus on according to the production plan.
Why we implemented our solution
Technicians felt involved and informed, because they had a clear view on future objectives and what is expected from them daily (what is being produced today, tomorrow, …).
Results
Technicians gain more autonomy and feel less reliant on the management.
To achieve the third goal, we did the following actions:
Our implementation
A supplier diagnostic visit and/or listing of spare parts based on the machine maintenance plans and the latest breakdowns.
Thanks to our partnership the maintenance team’s work efficiency improved.
The minimum required level of lines availability is reached (OEE), and we still aim to maintain this level and make it more stable.
Overall, improving OEE increased from 35% to 45%, which means an improvement in OEE by 10%.
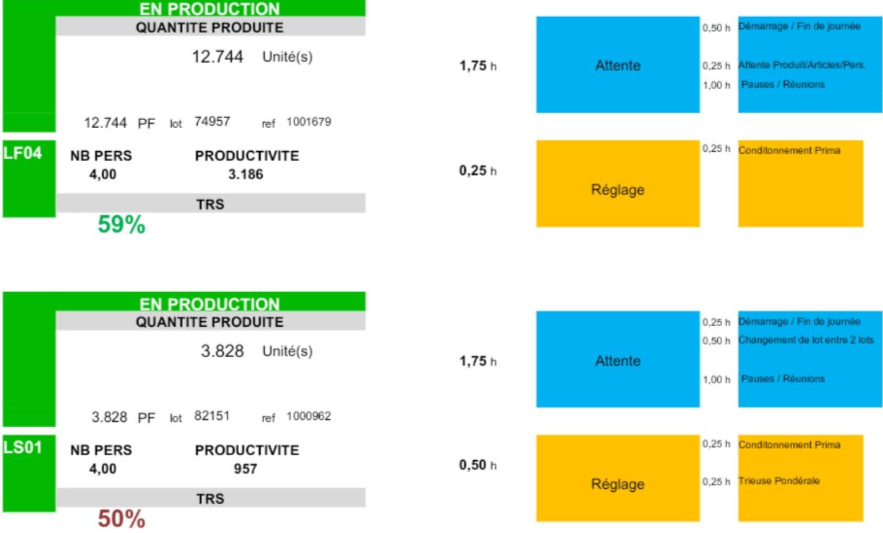
In addition, spare part requests made by technicians became easier due to the documentation and the available spare part list. This prevented wasted time due to, for example, the search for the spare part and the need for stopping the machine.
Finally, the overall maintenance operations enhanced.
The maintenance department can now focus more on continuous improvement, instead of only resolving emergencies and breakdowns.
➡️ Read our other success story, where we helped one of our clients to develop framework for predictive maintenance as a next step of continuous improvement